BADM Group Overview
BADM variables in this group are organized into subgroups as shown below. The overview highlights what variables are required per subgroup. It also indicates which variables cannot be specified together ( OR ) in the same group entry. Variables in "Applies to All" are included with all subgroups. See BADM Basics for more details.
Multiple entries of this BADM group can be reported per site. However, combinations of Ⓒ variables must be unique. Read more:
| Required | Optional | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Soil Organic Carbon Stock | ||||||||
Soil Total Nitrogen Stock | ||||||||
Soil NH4 Stock | ||||||||
Soil NO3 Stock | ||||||||
Soil Potassium Stock | ||||||||
Soil Phosphorus Stock | ||||||||
Applies to All |
BADM variables: Definitions, Units, Requirements
See Overview tab or BADM Basics for explanation of Required and Optional variables.
Multiple entries of this BADM group can be reported per site. However, combinations of Ⓒ variables must be unique. Read more:
| Variable Requirements | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SOIL_STOCK_C_ORG1-Required | g C m-2 | Soil organic carbon stock |
| SOIL_STOCK_C_ORG_STATISTICⒸ 1-Required | LIST(STATISTIC) Show | Soil organic carbon stock statistic The statistic for the measurement reported. Use predefined list (e.g., mean, min / max, standard deviation, etc). |
| SOIL_STOCK_C_ORG_STATISTIC_METHODⒸ 1-Optional | LIST(STATISTIC_METHOD) Show | Soil organic carbon stock statistic method Method used to generate the reported statistic (e.g., aggregate of individuals, aggregate of sample aggregates) from observations representing the same time period. Use predefined list. The aggregation method is not meant to describe temporal aggregations for example in calculations of higher frequency observations (e.g., sub-minute) to lower frequency observations (e.g., hourly) at a single location. |
| SOIL_STOCK_C_ORG_STATISTIC_NUMBER1-Optional | integer number | Number of observations used to determine soil organic carbon stock statistic Number of observations (samples / replicates) used to calculate the STATISTIC for the reported measurement. |
| SOIL_STOCK_N_TOT2-Required | g N m-2 | Soil total nitrogen stock |
| SOIL_STOCK_N_TOT_STATISTICⒸ 2-Required | LIST(STATISTIC) Show | Soil total nitrogen stock statistic The statistic for the measurement reported. Use predefined list (e.g., mean, min / max, standard deviation, etc). |
| SOIL_STOCK_N_TOT_STATISTIC_METHODⒸ 2-Optional | LIST(STATISTIC_METHOD) Show | Soil total nitrogen stock statistic method Method used to generate the reported statistic (e.g., aggregate of individuals, aggregate of sample aggregates) from observations representing the same time period. Use predefined list. The aggregation method is not meant to describe temporal aggregations for example in calculations of higher frequency observations (e.g., sub-minute) to lower frequency observations (e.g., hourly) at a single location. |
| SOIL_STOCK_N_TOT_STATISTIC_NUMBER2-Optional | integer number | Number of observations used to determine soil total nitrogen stock statistic Number of observations (samples / replicates) used to calculate the STATISTIC for the reported measurement. |
| SOIL_STOCK_NH43-Required | g NH4 m-2 | Soil ammonium stock |
| SOIL_STOCK_NH4_STATISTICⒸ 3-Required | LIST(STATISTIC) Show | Soil ammonium stock statistic The statistic for the measurement reported. Use predefined list (e.g., mean, min / max, standard deviation, etc). |
| SOIL_STOCK_NH4_STATISTIC_METHODⒸ 3-Optional | LIST(STATISTIC_METHOD) Show | Soil ammonium stock statistic method Method used to generate the reported statistic (e.g., aggregate of individuals, aggregate of sample aggregates) from observations representing the same time period. Use predefined list. The aggregation method is not meant to describe temporal aggregations for example in calculations of higher frequency observations (e.g., sub-minute) to lower frequency observations (e.g., hourly) at a single location. |
| SOIL_STOCK_NH4_STATISTIC_NUMBER3-Optional | integer number | Number of observations used to determine soil ammonium stock statistic Number of observations (samples / replicates) used to calculate the STATISTIC for the reported measurement. |
| SOIL_STOCK_NO34-Required | g NO3 m-2 | Soil nitrate stock |
| SOIL_STOCK_NO3_STATISTICⒸ 4-Required | LIST(STATISTIC) Show | Soil nitrate stock statistic The statistic for the measurement reported. Use predefined list (e.g., mean, min / max, standard deviation, etc). |
| SOIL_STOCK_NO3_STATISTIC_METHODⒸ 4-Optional | LIST(STATISTIC_METHOD) Show | Soil nitrate stock statistic method Method used to generate the reported statistic (e.g., aggregate of individuals, aggregate of sample aggregates) from observations representing the same time period. Use predefined list. The aggregation method is not meant to describe temporal aggregations for example in calculations of higher frequency observations (e.g., sub-minute) to lower frequency observations (e.g., hourly) at a single location. |
| SOIL_STOCK_NO3_STATISTIC_NUMBER4-Optional | integer number | Number of observations used to determine soil nitrate stock statistic Number of observations (samples / replicates) used to calculate the STATISTIC for the reported measurement. |
| SOIL_STOCK_K5-Required | g K m-2 | Soil potassium stock |
| SOIL_STOCK_K_STATISTICⒸ 5-Required | LIST(STATISTIC) Show | Soil potassium stock statistic The statistic for the measurement reported. Use predefined list (e.g., mean, min / max, standard deviation, etc). |
| SOIL_STOCK_K_STATISTIC_METHODⒸ 5-Optional | LIST(STATISTIC_METHOD) Show | Soil potassium stock statistic method Method used to generate the reported statistic (e.g., aggregate of individuals, aggregate of sample aggregates) from observations representing the same time period. Use predefined list. The aggregation method is not meant to describe temporal aggregations for example in calculations of higher frequency observations (e.g., sub-minute) to lower frequency observations (e.g., hourly) at a single location. |
| SOIL_STOCK_K_STATISTIC_NUMBER5-Optional | integer number | Number of observations used to determine soil potassium stock statistic Number of observations (samples / replicates) used to calculate the STATISTIC for the reported measurement. |
| SOIL_STOCK_P6-Required | g P m-2 | Soil phosphorus stock |
| SOIL_STOCK_P_STATISTICⒸ 6-Required | LIST(STATISTIC) Show | Soil phosphorus stock statistic The statistic for the measurement reported. Use predefined list (e.g., mean, min / max, standard deviation, etc). |
| SOIL_STOCK_P_STATISTIC_METHODⒸ 6-Optional | LIST(STATISTIC_METHOD) Show | Soil phosphorus stock statistic method Method used to generate the reported statistic (e.g., aggregate of individuals, aggregate of sample aggregates) from observations representing the same time period. Use predefined list. The aggregation method is not meant to describe temporal aggregations for example in calculations of higher frequency observations (e.g., sub-minute) to lower frequency observations (e.g., hourly) at a single location. |
| SOIL_STOCK_P_STATISTIC_NUMBER6-Optional | integer number | Number of observations used to determine soil phosphorus stock statistic Number of observations (samples / replicates) used to calculate the STATISTIC for the reported measurement. |
| SOIL_STOCK_PROFILE_ZERO_REFⒸ Optional | LIST(PROFILE_ZERO_REF) Show | Soil stock profile zero reference Profile Zero Reference is the horizontal plane from which the soil profile minimum and maximum depths are measured. For example, top of mineral soil or top of litter layer. Use predefined list. |
| SOIL_STOCK_PROFILE_MINⒸ Optional | cm | Soil stock profile minimum depth Profile minimum depth is the vertical distance from profile zero reference to the top of soil layer being measured. |
| SOIL_STOCK_PROFILE_MAXⒸ Optional | cm | Soil stock profile maximum depth Profile maximum depth is the vertical distance from profile zero reference to the bottom of soil layer being measured. |
| SOIL_STOCK_HORIZONOptional | free text | Soil stock profile horizon Use soil horizon scheme best suited for your soil. Examples include O, Oa, B, Bt, C. |
| SOIL_STOCK_APPROACHOptional | free text | Soil stock measurement approach |
| SOIL_STOCK_DATEⒸ Required | YYYYMMDDHHMM | Soil stock measurement sampling date Please report the date at the precision known. Allowed reporting precisions are YYYY, YYYYMM, YYYYMMDD, and YYYYMMDDHHMM. |
| SOIL_STOCK_DATE_UNCOptional | days | Uncertainty in the Soil stock measurement sampling date |
| SOIL_STOCK_COMMENTOptional | free text | Soil stock comments |
BADM Examples
Choose a variable marked with to show examples of how to submit and interpret these BADM. See BADM Basics for more details.
Combinations of Ⓒ variables must be unique. Read more: .
| Soil Organic Carbon Stock |
| Soil Total Nitrogen Stock |
| Soil NH4 Stock |
| Soil NO3 Stock |
| Soil Potassium Stock |
| Soil Phosphorus Stock |
| Applies to All |
STATISTIC Variables
Many BADM groups have a required and several optional STATISTIC variables. Specific examples of their use are given after an overview the variables basics.
STATISTIC Basics
BADM typically describe site-level descriptions and observations. The STATISTIC variables allow for full characterization of the reported information if desired. BADM groups, such as canopy height, LAI, soil chemistry, phenology, and biomass, contain the following STATISTIC variables:
| var_STATISTIC Required |
The type of value reported.
Options: |
| var_STATISTIC_METHOD Optional |
The method of aggregation used to generate the statistic.
Options: Statistics generated by this approach may represent spatial characteristics of the measurement within the site (e.g., spatial heterogeneity) and/or characteristics due to other factors (e.g., population variability). Aggregate of sample aggregates Statistics generated by this approach are often used to highlight the spatial characteristics within the site (i.e., the spatial heterogeneity of measurement within the site). Expert estimate See the Examples for more details. |
| var_STATISTIC_NUMBER Optional |
The number of observations used in calculating the statistic. |
STATISTIC Examples
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area

For DBH observations of individual trees in a single sample area at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots
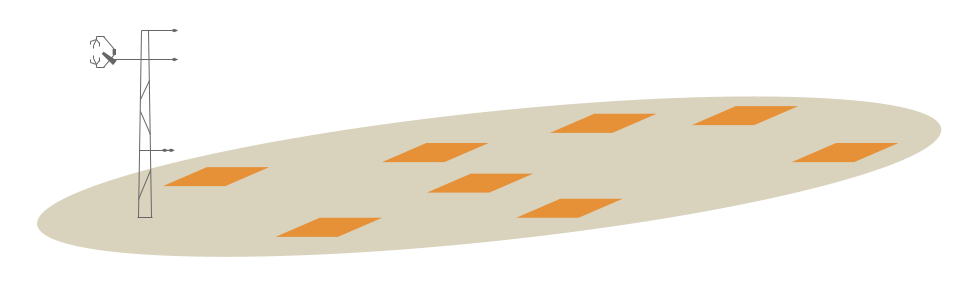
For DBH observations of individual trees in 8 sample plots at the site:
If the individual DBH observations are first aggregated at the plot level and then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs to highlight spatial variability:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If the individual DBH observations are aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site

For DBH observations of individual trees randomly selected at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots

For Biomass observations collected from 5 sub-plots located in each of 8 sample plots at the site:
In many cases, the sub-plot biomass observations are first aggregated at the plot level. Then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If pseudo-replication or spatial autocorrelation is not an issue, the sub-plot observations may be aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 40
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations
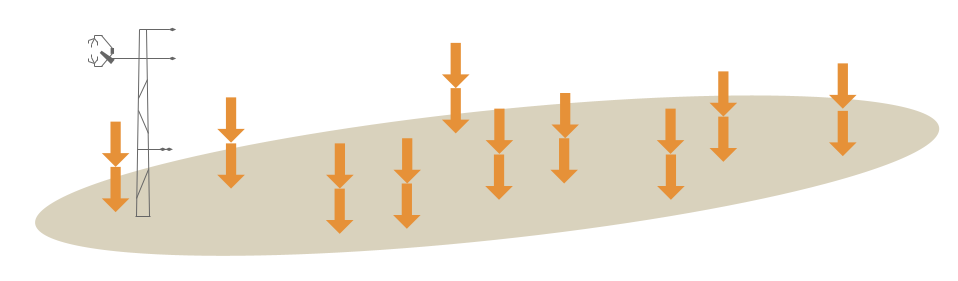
For replicate soil carbon observations at 10 randomly-selected points within the site:
To calculate Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, and Standard Deviation, the replicates at each location should first be averaged. Then the average values at each location can be used to calculate the STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
The average difference between the replicates can be used to estimate the Measurement Uncertainty:
STATISTIC = Measurement Uncertainty
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
STATISTIC Variables
Many BADM groups have a required and several optional STATISTIC variables. Specific examples of their use are given after an overview the variables basics.
STATISTIC Basics
BADM typically describe site-level descriptions and observations. The STATISTIC variables allow for full characterization of the reported information if desired. BADM groups, such as canopy height, LAI, soil chemistry, phenology, and biomass, contain the following STATISTIC variables:
| var_STATISTIC Required |
The type of value reported.
Options: |
| var_STATISTIC_METHOD Optional |
The method of aggregation used to generate the statistic.
Options: Statistics generated by this approach may represent spatial characteristics of the measurement within the site (e.g., spatial heterogeneity) and/or characteristics due to other factors (e.g., population variability). Aggregate of sample aggregates Statistics generated by this approach are often used to highlight the spatial characteristics within the site (i.e., the spatial heterogeneity of measurement within the site). Expert estimate See the Examples for more details. |
| var_STATISTIC_NUMBER Optional |
The number of observations used in calculating the statistic. |
STATISTIC Examples
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area

For DBH observations of individual trees in a single sample area at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots

For DBH observations of individual trees in 8 sample plots at the site:
If the individual DBH observations are first aggregated at the plot level and then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs to highlight spatial variability:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If the individual DBH observations are aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site

For DBH observations of individual trees randomly selected at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots

For Biomass observations collected from 5 sub-plots located in each of 8 sample plots at the site:
In many cases, the sub-plot biomass observations are first aggregated at the plot level. Then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If pseudo-replication or spatial autocorrelation is not an issue, the sub-plot observations may be aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 40
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations

For replicate soil carbon observations at 10 randomly-selected points within the site:
To calculate Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, and Standard Deviation, the replicates at each location should first be averaged. Then the average values at each location can be used to calculate the STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
The average difference between the replicates can be used to estimate the Measurement Uncertainty:
STATISTIC = Measurement Uncertainty
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
STATISTIC Variables
Many BADM groups have a required and several optional STATISTIC variables. Specific examples of their use are given after an overview the variables basics.
STATISTIC Basics
BADM typically describe site-level descriptions and observations. The STATISTIC variables allow for full characterization of the reported information if desired. BADM groups, such as canopy height, LAI, soil chemistry, phenology, and biomass, contain the following STATISTIC variables:
| var_STATISTIC Required |
The type of value reported.
Options: |
| var_STATISTIC_METHOD Optional |
The method of aggregation used to generate the statistic.
Options: Statistics generated by this approach may represent spatial characteristics of the measurement within the site (e.g., spatial heterogeneity) and/or characteristics due to other factors (e.g., population variability). Aggregate of sample aggregates Statistics generated by this approach are often used to highlight the spatial characteristics within the site (i.e., the spatial heterogeneity of measurement within the site). Expert estimate See the Examples for more details. |
| var_STATISTIC_NUMBER Optional |
The number of observations used in calculating the statistic. |
STATISTIC Examples
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area

For DBH observations of individual trees in a single sample area at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots

For DBH observations of individual trees in 8 sample plots at the site:
If the individual DBH observations are first aggregated at the plot level and then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs to highlight spatial variability:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If the individual DBH observations are aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site

For DBH observations of individual trees randomly selected at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots

For Biomass observations collected from 5 sub-plots located in each of 8 sample plots at the site:
In many cases, the sub-plot biomass observations are first aggregated at the plot level. Then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If pseudo-replication or spatial autocorrelation is not an issue, the sub-plot observations may be aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 40
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations

For replicate soil carbon observations at 10 randomly-selected points within the site:
To calculate Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, and Standard Deviation, the replicates at each location should first be averaged. Then the average values at each location can be used to calculate the STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
The average difference between the replicates can be used to estimate the Measurement Uncertainty:
STATISTIC = Measurement Uncertainty
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
STATISTIC Variables
Many BADM groups have a required and several optional STATISTIC variables. Specific examples of their use are given after an overview the variables basics.
STATISTIC Basics
BADM typically describe site-level descriptions and observations. The STATISTIC variables allow for full characterization of the reported information if desired. BADM groups, such as canopy height, LAI, soil chemistry, phenology, and biomass, contain the following STATISTIC variables:
| var_STATISTIC Required |
The type of value reported.
Options: |
| var_STATISTIC_METHOD Optional |
The method of aggregation used to generate the statistic.
Options: Statistics generated by this approach may represent spatial characteristics of the measurement within the site (e.g., spatial heterogeneity) and/or characteristics due to other factors (e.g., population variability). Aggregate of sample aggregates Statistics generated by this approach are often used to highlight the spatial characteristics within the site (i.e., the spatial heterogeneity of measurement within the site). Expert estimate See the Examples for more details. |
| var_STATISTIC_NUMBER Optional |
The number of observations used in calculating the statistic. |
STATISTIC Examples
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area

For DBH observations of individual trees in a single sample area at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots

For DBH observations of individual trees in 8 sample plots at the site:
If the individual DBH observations are first aggregated at the plot level and then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs to highlight spatial variability:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If the individual DBH observations are aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site

For DBH observations of individual trees randomly selected at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots

For Biomass observations collected from 5 sub-plots located in each of 8 sample plots at the site:
In many cases, the sub-plot biomass observations are first aggregated at the plot level. Then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If pseudo-replication or spatial autocorrelation is not an issue, the sub-plot observations may be aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 40
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations

For replicate soil carbon observations at 10 randomly-selected points within the site:
To calculate Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, and Standard Deviation, the replicates at each location should first be averaged. Then the average values at each location can be used to calculate the STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
The average difference between the replicates can be used to estimate the Measurement Uncertainty:
STATISTIC = Measurement Uncertainty
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
STATISTIC Variables
Many BADM groups have a required and several optional STATISTIC variables. Specific examples of their use are given after an overview the variables basics.
STATISTIC Basics
BADM typically describe site-level descriptions and observations. The STATISTIC variables allow for full characterization of the reported information if desired. BADM groups, such as canopy height, LAI, soil chemistry, phenology, and biomass, contain the following STATISTIC variables:
| var_STATISTIC Required |
The type of value reported.
Options: |
| var_STATISTIC_METHOD Optional |
The method of aggregation used to generate the statistic.
Options: Statistics generated by this approach may represent spatial characteristics of the measurement within the site (e.g., spatial heterogeneity) and/or characteristics due to other factors (e.g., population variability). Aggregate of sample aggregates Statistics generated by this approach are often used to highlight the spatial characteristics within the site (i.e., the spatial heterogeneity of measurement within the site). Expert estimate See the Examples for more details. |
| var_STATISTIC_NUMBER Optional |
The number of observations used in calculating the statistic. |
STATISTIC Examples
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area

For DBH observations of individual trees in a single sample area at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots

For DBH observations of individual trees in 8 sample plots at the site:
If the individual DBH observations are first aggregated at the plot level and then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs to highlight spatial variability:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If the individual DBH observations are aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site

For DBH observations of individual trees randomly selected at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots

For Biomass observations collected from 5 sub-plots located in each of 8 sample plots at the site:
In many cases, the sub-plot biomass observations are first aggregated at the plot level. Then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If pseudo-replication or spatial autocorrelation is not an issue, the sub-plot observations may be aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 40
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations

For replicate soil carbon observations at 10 randomly-selected points within the site:
To calculate Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, and Standard Deviation, the replicates at each location should first be averaged. Then the average values at each location can be used to calculate the STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
The average difference between the replicates can be used to estimate the Measurement Uncertainty:
STATISTIC = Measurement Uncertainty
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
STATISTIC Variables
Many BADM groups have a required and several optional STATISTIC variables. Specific examples of their use are given after an overview the variables basics.
STATISTIC Basics
BADM typically describe site-level descriptions and observations. The STATISTIC variables allow for full characterization of the reported information if desired. BADM groups, such as canopy height, LAI, soil chemistry, phenology, and biomass, contain the following STATISTIC variables:
| var_STATISTIC Required |
The type of value reported.
Options: |
| var_STATISTIC_METHOD Optional |
The method of aggregation used to generate the statistic.
Options: Statistics generated by this approach may represent spatial characteristics of the measurement within the site (e.g., spatial heterogeneity) and/or characteristics due to other factors (e.g., population variability). Aggregate of sample aggregates Statistics generated by this approach are often used to highlight the spatial characteristics within the site (i.e., the spatial heterogeneity of measurement within the site). Expert estimate See the Examples for more details. |
| var_STATISTIC_NUMBER Optional |
The number of observations used in calculating the statistic. |
STATISTIC Examples
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations
Example 1: DBH calculated from a single sampling area

For DBH observations of individual trees in a single sample area at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 2: DBH calculated from 8 plots

For DBH observations of individual trees in 8 sample plots at the site:
If the individual DBH observations are first aggregated at the plot level and then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs to highlight spatial variability:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If the individual DBH observations are aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 3: DBH calculated from randomly selected trees within the site

For DBH observations of individual trees randomly selected at the site:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = # of individual samples
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 4: Biomass calculated from 8 plots each with 5 sub-plots

For Biomass observations collected from 5 sub-plots located in each of 8 sample plots at the site:
In many cases, the sub-plot biomass observations are first aggregated at the plot level. Then the plot values are are used to calculate the site-level STATISTICs:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 8
If pseudo-replication or spatial autocorrelation is not an issue, the sub-plot observations may be aggregated across all plots to calculate the site-level STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 40
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
Example 5: Soil carbon calculated from replicate samples at 10 locations

For replicate soil carbon observations at 10 randomly-selected points within the site:
To calculate Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, and Standard Deviation, the replicates at each location should first be averaged. Then the average values at each location can be used to calculate the STATISTIC:
STATISTIC* = Mean, Minimum, Maximum, Percentiles, or Standard Deviation
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of sample aggregates
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
* Minimum, Maximum, and Percentiles should only be calculated if the sample size is adequately large.
The average difference between the replicates can be used to estimate the Measurement Uncertainty:
STATISTIC = Measurement Uncertainty
STATISTIC_METHOD = Aggregate of individual observations
STATISTIC_NUMBER = 10
DATE and DATE_UNC
DATE
Many groups require DATE to describe the time period that the metadata or ancillary data represents.
Dates should be entered at the precision known and most suitable to the observation. Supported precision include year, month, day, and minute in ISO formats: YYYY, YYYYMM, YYYYMMDD, YYYYMMDDHHMM.
Typical resolutions used for DATE are year, month, or day: YYYY, YYYYMM, YYYYMMDD.
DATE_UNC
Uncertainty in the DATE is an optional variable that can also be reported.
Report a date uncertainty that is commensurate with the DATE reported. For example if a day is reported for the DATE, date uncertainty should be on the order of days rather than months or years. If a year is reported for the DATE, date uncertainty should be greater than a year.
Customize and Download CSV for BADM Submission
Select variables from one or more subgroups to form a complete group. At a minimum, the required variables from the “Applies to All” subgroup must be included in every group. After selecting your desired variables, download the customized CSV file for submission of BADM. For additional submission details, see BADM Submission Instructions.
Multiple entries of this BADM group can be reported per site. However, combinations of Ⓒ variables must be unique. Read more: . See BADM Basics for more details.
| Required | Optional | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| Required | Optional | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| Required | Optional | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| Required | Optional | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| Required | Optional | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| Required | Optional | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| Required | Optional | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Submit completed CSV file at Upload Data using the BADM option (login required).
