The AmeriFlux Tech Team has developed and started testing a portable profile system to quantify canopy storage of CO2 and energy. The team has deployed the system at a number of site visits during the 2016 and 2017 field season. We highlight the system design, components, and early results.
The portable profile system was designed and built by Chad Hanson. The following text and figures were adapted from a poster presented by Chad during the 2016 AGU fall meeting.
Program Goals
The AmeriFlux portable profile system (PPS) was built to understand and improve how storage is being measured as a complimentary activity to site visits by the Tech Team.
The purpose of this new program is to
- Provide a high quality reference measurement of CO2 storage
- Provide diagnostic data and analysis of the site characteristics with regard to layer heights, inlet placement, and sampling frequency
- Promote the importance of measuring the storage term within AmeriFlux.
Portable Profile System
In order to achieve the goals of high performance, portability, and diagnostic power, the profile system uses high spatial coverage and frequent sampling rates.
Inlet description
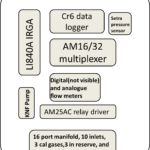
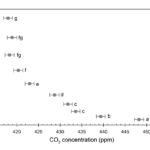
The PPS utilizes 10 measurement heights that are spaced according to an exponential function, hi = (nib*Z)*nt-b. Where hi is the height of the inlet, ni is the number of the inlet from the ground, Z is the eddy covariance measurement height, nt is the total number of inlets and b is an exponent (~2). Inlets are placed on 1 m booms to minimize tower influence, and are co-located with an aspirated temperature sensor (Apogee ST-110 thermistors housed in TS-100 shields). Inlets flow continuously to the PPS and are sub-sampled by a LI-840 IRGA via a valve switching manifold for 30 seconds every 5 minutes.
Primary measurements
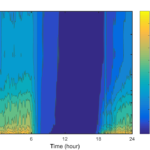
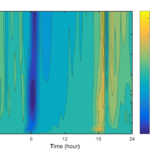
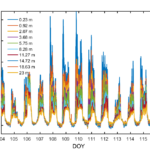
The first 15 seconds of every interval is discarded to eliminate any valve switching effects and to allow the manifold to purge. This yields six whole column measurements for each half hour period. Pressure is measured at the base of the tower and corrected for each height. Water vapor pressure is derived from the IRGA H2O values and used in combination with the temperature and pressure data to correct the IRGA CO2 values to density in dry air. Whole column averages of CO2 density are calculated by weighting each inlet’s contribution according to the thickness of the layer it represents.
Storage calculation
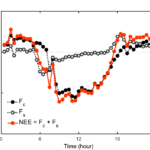
Canopy storage (Sc) is calculated as the change in column density between 30 min periods. For convenience when relating to EC data, Sc is reported in µmol m2 s-1. Sc = ∫(δc/δt) dh where c is CO2 density, t is time, and h is the height of eddy covariance system. The integral is evaluated from 0 to h in discrete layers according to the inlet heights.
PPS parts lists
A comprehensive list of all major components parts can be found on the following speadsheet.
PPS images and example figures
- PPS interior
- PPS interior valves
- PPS exterior bottom
- PPS deployment at US-TON
- PPS deployment at US-TON
- PPS parts schematic
- PPS vertical gradient of CO2
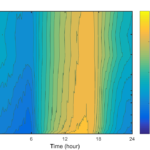
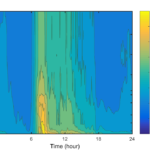
- PPS diurnal CO2 contour
- PPS diurnal CO2 change with time contour
- PPS CO2 time series
- PPS diurnal air temperature contour
- PPS diurnal H2O contour






No Comments
Be the first to start a conversation